Term two topics
Classification of Matter
- States of Matter
- Kinetic Theory of Matter
Elements, compounds and mixtures
Solutions and Suspensions
Separation Techniques
Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter
The kinetic theory of matter states that all matter is made up of a large number of tiny atoms or molecules which are in continuous motion.
The existence of particles in constant motions is prove by Brownian motion and diffusion. Diffusion is the spreading of the particles without
other factors such as wind. When a bottle of perfume is opened, the smell of the perfume will fill up the room in a while. This shows that the
perfume molecules have traveled around the air and prove the kinetic theory of matter. (Experiment has been done in class in term two)
Molecular Model of the Three States of Matter
Solid:
The molecules of the solid are packed together tightly. They have strong attraction and repelling force among themselves which prevent them from collapsing.
Therefore, this explain why the solid is always is fixed shape and have fixed volume. Solid cannot be compressed because there is very little gaps between the molecules.
Liquid:
The molecules of the solid are further apart than the solid. However, the molecules of the liquid can move around within the liquid. Hence, the liquid do not have fix shape. The
strong attraction force is still able to keep the liquid together so the liquid has a definite volume.
Gas:
The molecules of the gas are far apart. They move randomly with high speed. Therefore, a gas do not have definite shape and volume and can be compressed easily due to the huge space between the molecules.


Element, Compound and mixture
Element:
Element is the simplest substance. It cannot be brkoen down into simpler substance by any physical or chemical methods. Symbols of elements that have been discovered so far are on the periodic table.Elements located on the same horizontal line is called "period" while elements on the same vertical line is called "group". Elements
on the same group have similiar chemical properties.
The Zigzag line differentiate metal and non-metal elements. The elements on the right are non-metal while the elements on the left are
metal.
Metal and non-metal can be differentiate easily by their properties. (Below shows a comparison between metal and non-metal)

Compound:
A compound is two or more elements that are join together by chemical methods. They are formed by fixed proportion and do not
have the properties of its constituent elements.
Compound can only be separated by chemical methods such as electrolysis.
One of the example of compund is magnesium oxide. Magnesium oxide is formed when burning magnesium in air. The magnesium has
combined with oxygen in the air when burning, produce bright light and strong heat. (Experiment done in term 2)Mixture:
Elements in mixture is not combined together. Hence, mixture is not formed by fix proportion and have the properties of its constituent
elments. They do not have fixed boiling point also and can be broken down into simpler substances by physical methods.
Example: Air
Solution and Suspension
Solution:
A solution is a homogeneous mixture whereby solute has dissolved completely in solvent.
Solute: It is the one which is going to be dissolved
Solvent: It dissolved the solute
Types of solution:
Dilute solution: There is little amount of solute inside the solvent. Low concentration.
Concentrated solution: There is large amount of solute inside the solvent. High concentration.
Saturated solution: Maximum amount of solute inside the solvent. Maximum concentration. No solute can be dissolved anymore.
Properties: (apply on liquid solution)
- Clear and allow light to pass through
- Solute will not sink to the bottom after left un-touch for a while
- No filtrate on the filter paper after filtration
Suspension:
A suspension is a non-homeogenous mixture whereby the solute cannot be dissolve in the solvent.
Properties:
- Unclear and do not allow light to pass through
- Solute will sink to the bottom after left un-touch for a while
- Solute will be left on the filter paper after filtration
Solubility:
Solubility refers to the solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent.
Factors that will affect solubility:
- Type of solvent
- Type of solute
- Temperature
Rate of dissolving
Rate of dissolving is the time taken for the solute to dissolve completely in solvent.
Factors that will affect the rate of dissolving:
- Size of the solute
- Temperature of solution
- Rate of stirring
Separation Techniques
Filtration:
It is used to separate a solid from a liquid.

How to separate?
- Set up the experiment set up as shown on the picture above
- Pour the mixture of solution into the funnel
- The solute which is insoluble will be left on the filter papar, they are called residue
- The solution will be gathered in the beaker
Crystallization
It is used to recover pure soluble solid from a solution which is not heat-stable
Steps:
The solution is heated until it becomes saturated
It is allow to cool down so that crystals can be formed
If a compound is not heat-stable,strong heating to dryness would decompose it
Example: Sugar crystals are not heat-stable. They can only be obtained by crystallization. Evaporation to dryness will decompose the sugar crystals to carbon.
Simple distillation
It is used to separate a solid-liquid mixture.

Steps:
The liquid is heated until its boiling point and changes into a vapour
the vapour is then cooled by a condenser and changes back into a liquid
It is collected in the receiver as a distillate
The impurities which have much higher boiling points remain in the flask
The bulb of the thermometer must be placed near the opening of the condenser so that it can measure the boiling point of the substances accurately
During the boiling of a substance, the temperature remains constant
EXTRA: Boiling chips inside the distillation flask is used to ensure smooth boiling.
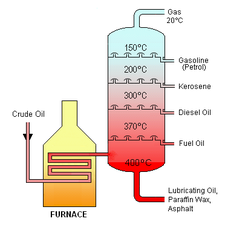
Fractional Distillation
It is used to separated a liquid-liquid mixture which is miscible
It can only be used if liquids have different boiling points
A tall fractional column is used in fractional distillation. It allow the separation of different liquids more efficiently
The substance with a lower boiling point is distilled first
Fractional distillation is used largely in the following industries: Separation of liquid air and Separation of crude oil or petroleum

Paper Chromatography
It is used to separate a mixture which is based on the extent of solubility in a given solvent.
There are different techniques in chromatography. Paper chromatography is the common techniques used in the school laboratory.

The more soluble the component in the solvent, the further the distance it travels in the chromatography paper.
The advantages of using chromatography